
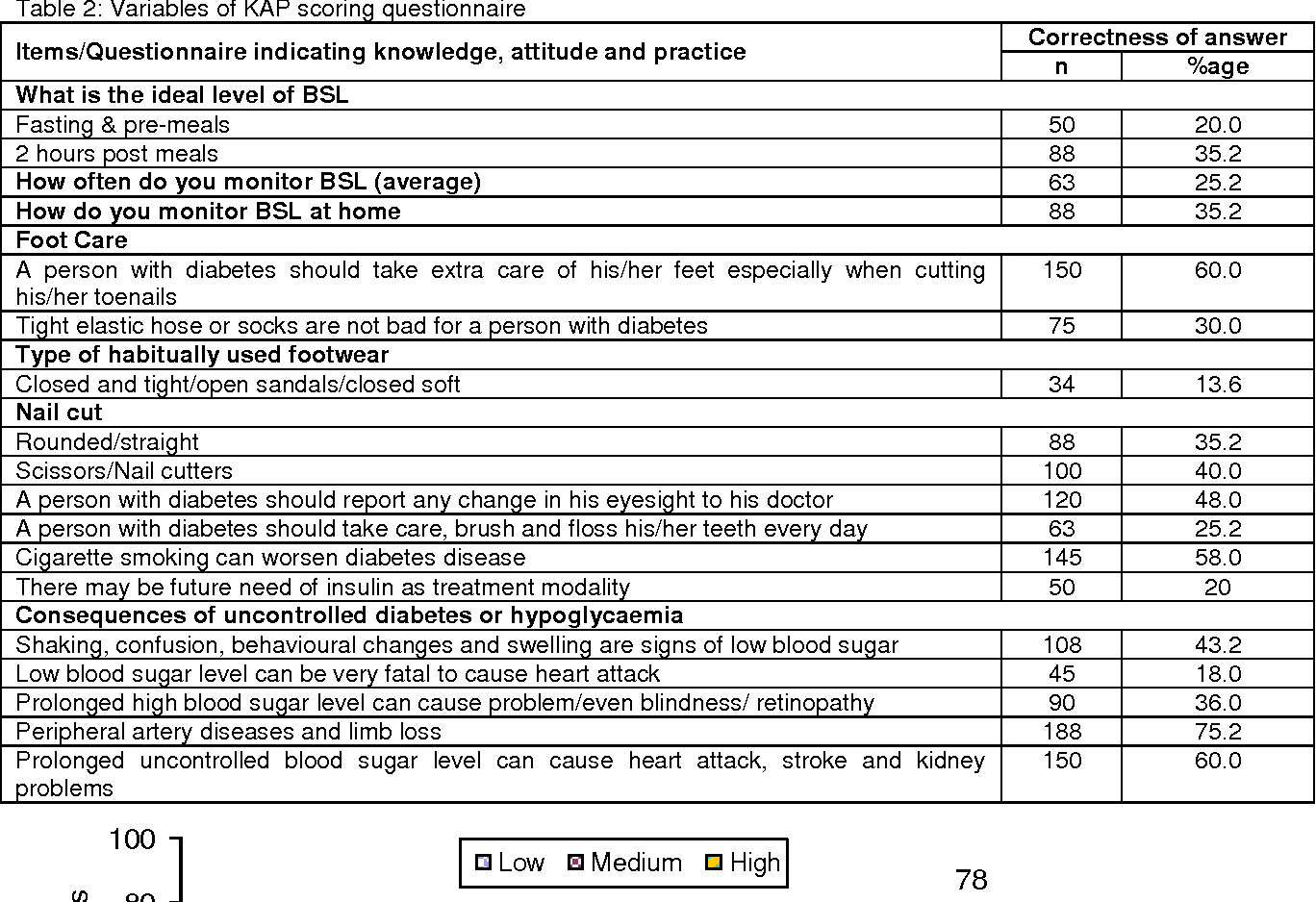
Thus, effective strategies should be implemented to prevent further increase of hypertension. Apart from that, an increase in body weight and blood level glucose, triglycerides, and albumin too enhanced the risk of high blood pressure in Malaysian elderly ( 12). Excessive dietary sodium intake is associated with an increased risk of hypertension, which in turn may be a major risk factor of stroke, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and kidney diseases ( 11). Another study by Apidechkul ( 10) toward elderly in the rural area of Thailand revealed that high salt intake was the factor causing hypertension. Although it is found that poor knowledge contributes to higher salt consumption, the reason behind such result is unknown. The high sodium consumption among Malaysians were reported to be a result of poor knowledge and practice toward reducing salt intake ( 8). reported poor hypertensive control among Malaysians with hypertension was related to high salt diet eating habits ( 9). A significant contributor to the daily intake of sodium in Malaysia was found to be in sauces and cooked food ( 7, 8). Risk factors of hypertension included Body Mass Index (BMI), smoking, arterial stiffness and resistance, and high dietary salt or sodium intake ( 6).
Despite the alarming prevalence, the awareness toward hypertension and factors related to it is still low ( 5). Previous analysis based on the National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2018 by The Institute for Public Health (IKU) ( 4) showed that the prevalence of hypertension among pre-elderly in Malaysia was 32.7% with 77.3% pre-elderly reportedly had hypertension screening in the past 12 months ( 4). More than half of the population aged 65 years old and above in Malaysia has hypertension ( 3). Prevalence of hypertension increases with age and most are asymptomatic at least until the early stage. The prevalence of hypertension in Malaysia (i.e., 22.9%) is reported to be higher than its neighboring countries, i.e., Singapore (14.6%) and Thailand (22.3%) ( 2). The World Health Organization (WHO) predicted that 1.56 billion (29.2% of the world population) will develop hypertension by 2025. Further education and intervention is required to improve knowledge on healthy salt intake among elderly as part of the prevention from hypertension.Ī recent study by NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (2017) ( 1) revealed that Asian countries, especially industrial countries are facing a threat for a hypertension epidemic. Overall, this study showed that knowledge toward healthy salt intake, BMI, education level, and living with others were significantly associated with the blood pressure among the elderly. Younger age, higher level of education and living partner or elderly was significantly ( p < 0.05) associated with lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure. BMI was found to have significant correlation with blood pressure ( r = 0.278, p 0.05) with blood pressure. However, majority showed a positive attitude toward reducing the salt intake. Results indicated that the overall KAP score was average (57.4%). A total of 94 elderly have participated in the study. Anthropometry parameters and blood pressure were measured.

Subjects were required to answer the questionnaire via face to face interview regarding KAP of Salt Intake, together with sociodemographic and health profiles. A cross-sectional study using convenience sampling was conducted among Malay elderly, aged 60–81 years old residing in Bandar Baru Bangi. Therefore, this study was aimed to determine the association of KAP of healthy salt intake toward blood pressure among the elderly residing in a semi urban area of Klang Valley Malaysia. Improving the knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) related to salt intake is a key component of effective blood pressure control. Public exposure to a high salt diet has contributed to the increase in prevalence of hypertension among the Malaysian population.
Hypertension is a worldwide problem and a major global health burden with high salt intake as one of the factors often related to it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
